Critical Concept Distinctions That Separate the FAPI Marketing Framework from Traditional Marketing Management
Modern marketing is evolving fast, and with it, the expectations placed on marketing leaders, teams, and systems. While traditional marketing management has shaped decades of practice, the FAPI Marketing Framework introduces a fundamentally different—and far more advanced—approach to delivering marketing performance at scale.
Below is a breakdown of the four most significant conceptual distinctions between FAPI-driven marketing management and the traditional model—each directly aligned to one of the four modules of the FAPI Framework: Frame, Architecture, Production, and Insights. Together, these distinctions explain why FAPI creates more predictable outcomes, higher-performing teams, and stronger alignment with business strategy.
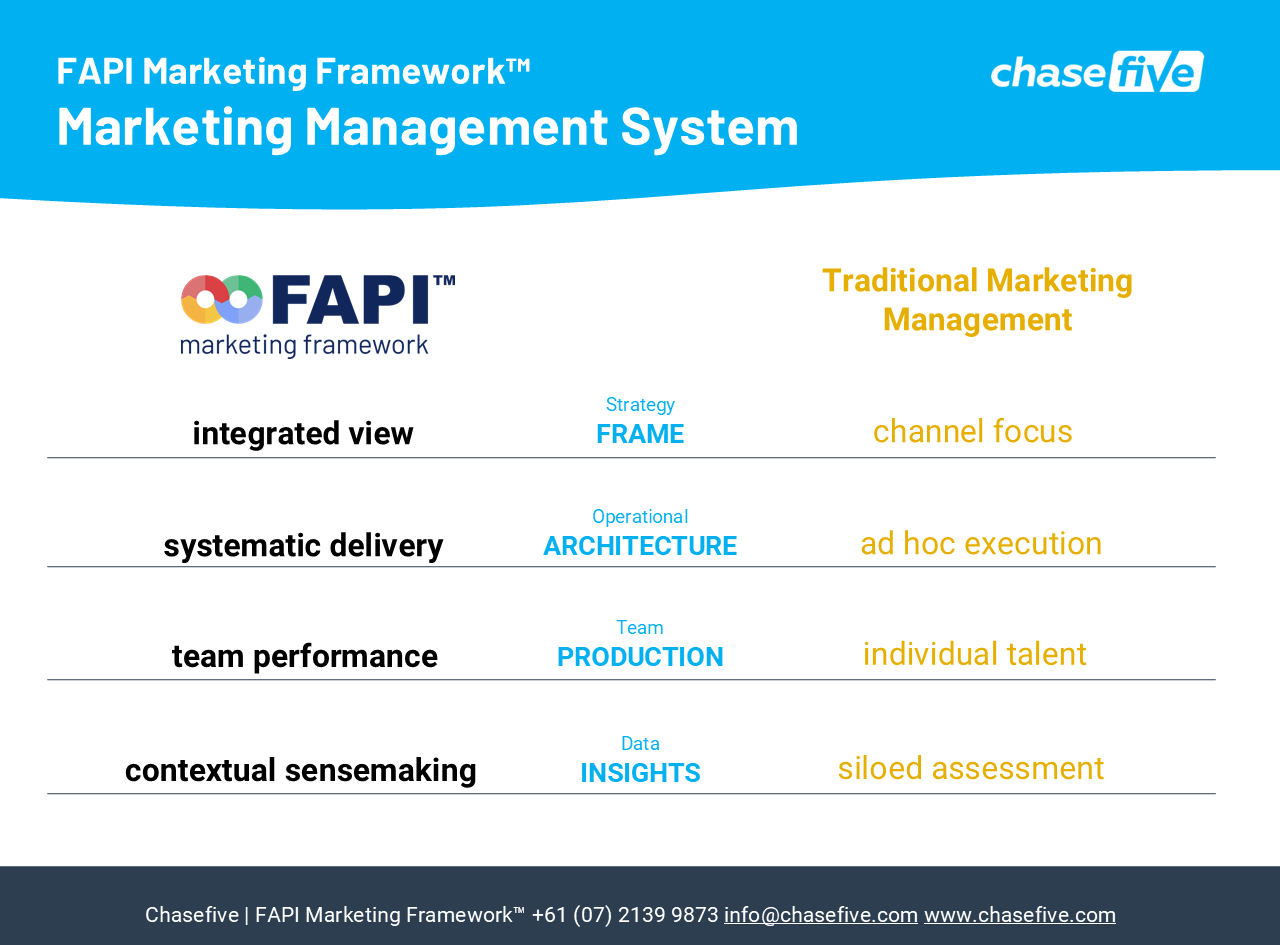
1. Integrated View vs. Channel Focus (Frame Module)
FAPI (Frame Module): Integrated View
The Frame module establishes the strategic foundation for the entire marketing function, and with it, the requirement for a holistic, integrated view of marketing.
Marketing is treated as a connected ecosystem where customer journey stages, channels, campaigns, and operations are unified beneath one strategic direction. This ensures:
- Consistent customer experiences
- Seamless messaging across all touchpoints
- More efficient allocation of resources
- One coherent narrative across the business
The Frame module prevents fragmented thinking by enforcing a single source of strategic truth, ensuring every activity aligns with the overarching business ambition.
Traditional: Channel Focus
Traditional marketing teams are often structured and measured by channel—“the email team,” “the social team,” “the events team.”
This creates common issues:
- Competing priorities
- Conflicting messages
- Data sitting in silos
- Success defined by channel-level metrics rather than business outcomes
FAPI corrects this by ensuring strategy is unified from the top, eliminating channel-driven fragmentation before it begins.
2. Systematic Delivery vs. Ad Hoc Execution (Architecture Module)
FAPI (Architecture Module): Systematic Delivery
The Architecture module converts the strategic Frame into a fully designed,
operational marketing plan. This is where FAPI’s emphasis on systematic delivery becomes clear.
Marketing is not a collection of spontaneous tasks—it is a designed, repeatable, end-to-end operational system. Every initiative follows a defined workflow with clear accountabilities and structured handoffs.
This systematic approach:
- Reduces waste and duplication
- Eliminates reactivity and last-minute improvisation
- Ensures a consistent transition from strategy to execution
- Aligns every activity with the strategic Frame
Traditional: Ad Hoc Execution
Traditional marketing often runs on urgency, intuition, or reactive demand. Work is initiated without a clear system or structural link to strategy.
As a result:
- Quality varies widely
- Knowledge remains undocumented
- Teams struggle to scale successful initiatives
- Performance depends on improvisation, not process
The Architecture module professionalises marketing by replacing ad hoc execution with predictable, accountable operational design.
3. Team Performance vs. Individual Talent (Production Module)
FAPI (Production Module): Team Performance
The Production module is where the designed system is delivered. FAPI positions team performance—not individual heroics—as the engine of consistent execution.
Roles such as the
Plan Master,
Functional Leads, and
Production Executives work in a
coordinated marketing structure where responsibilities are shared, documented, and measurable.
This creates:
- High-performing teams that deliver at scale
- Predictable outcomes regardless of turnover
- Reduced dependency on “star players”
- Workflows that are resilient and repeatable
Traditional: Individual Talent
In traditional marketing, success often depends on the capabilities, creativity, or institutional knowledge of a few standout individuals.
This leads to:
- Bottlenecks
- Fragile performance
- Siloed expertise
- Inconsistent delivery
The Production module eliminates personality-driven marketing and replaces it with system-driven performance.
4. Contextual Sensemaking vs. Isolated Analysis (Insights Module)
FAPI (Insights Module): Contextual Sensemaking
The Insights module transforms reporting into strategic intelligence. Performance data is interpreted through the full context of business goals, market conditions, and strategic direction—not just channel metrics.
This creates:
- A self-correcting marketing system
- Continuous improvement loops
- Insights that feed directly back into the Frame and Architecture
- Clear visibility of marketing’s impact on commercial outcomes
Traditional: Isolated Analysis
Traditional analysis often focuses on narrow metrics—open rates, click-through rates, impressions—without linking them back to strategy or business value.
This results in:
- Reporting with no strategic relevance
- Activity measurement rather than impact measurement
- Difficulty demonstrating marketing ROI to leadership
The Insights module elevates analytics from operational reporting to strategic sensemaking.
Conclusions
The FAPI Marketing Framework represents the next stage in marketing maturity.
By shifting:
- from channel silos to a unified strategic Frame,
- from ad hoc execution to a designed Architecture,
- from individual heroics to Production-driven team performance,
- from metrics in isolation to strategic Insights.
FAPI delivers a more resilient, scalable, and commercially aligned model for modern marketing management.
For organisations seeking operational clarity, predictable performance, and stronger strategic alignment, these four distinctions mark the path forward.
Learn more about marketing management at the FAPI Marketing Framework Academy







