Marketing performance metrics layers. Providing clarity in marketing decision-making
The objective of analyzing marketing data is to optimize performance. Therefore, marketing data and analysis are valuable only when they are translated into actionable improvements. However, this requires clear communication and understanding or marketing metrics by budget owners and decision-makers.
The FAPI Marketing Framework emphasizes the importance of separating marketing metrics for different stakeholders to enhance clarity and decision-making.
This approach ensures that each stakeholder can access and analyze the marketing metrics relevant to their specific roles and responsibilities, allowing them to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions that align with the organization's overall marketing objectives.
The starting point is to categorize marketing performance reporting into three distinct layers, each tailored to serve a specific audience within the organization.
- Commercial Marketing Metrics
- Marketing-Management Metrics
- Marketing-Production Metrics
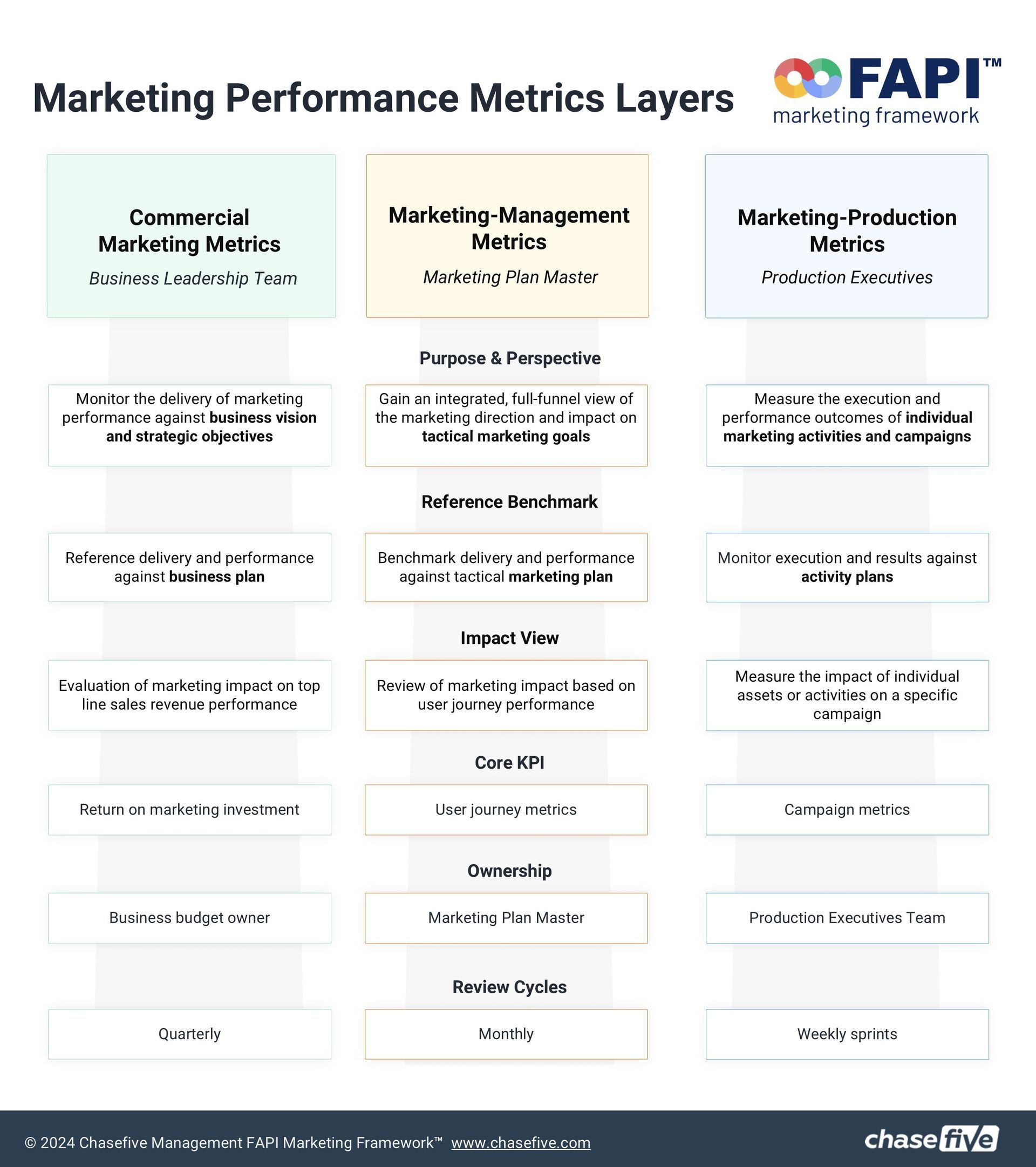
1. Commercial marketing metrics (for business leadership teams)
Commercial metrics are designed for business leadership teams and focus on monitoring marketing performance against the company's overarching business vision and strategic objectives.
Key metrics include Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI) and the impact on top-line revenue. Reports are typically reviewed quarterly to align with broader business planning.
This layer focuses on monitoring the delivery of marketing performance against the overarching business vision and strategic objectives.
The emphasis is on aligning marketing efforts with the broader business goals.
Performance is benchmarked against the business plan, ensuring that the marketing department is contributing effectively to the company's overall strategy. This includes an evaluation of marketing's impact on top-line revenue, providing insights into how marketing activities drive financial outcomes.
The primary KPI at this level is the Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI), which measures the efficiency and profitability of marketing expenditures.
Typically, the business budget owner or senior leadership team would own this reporting layer, as it directly influences strategic decision-making.
Reports in this layer are generally reviewed on a quarterly basis, aligning with broader business planning and review cycles.
2. Marketing-management metrics (for Plan Master)
Tailored to the marketing management role (Plan Master), these metrics provide a full-funnel view of marketing's impact on tactical goals. They benchmark performance against the tactical marketing plan and track user journey metrics.
The focus here is on gaining an integrated, full-funnel view of the marketing direction and impact on tactical marketing goals. This layer bridges the gap between strategic objectives and day-to-day marketing operations.
Performance is benchmarked against the tactical marketing plan, ensuring that all marketing efforts are aligned with tactical objectives and campaign goals.
This layer reviews the marketing impact based on user journey performance, providing insights into how well the marketing activities are guiding potential customers through the sales funnel.
The key performance indicators here include User Journey Metrics, which help in understanding how effectively the marketing activities engage and convert prospects.
The Plan Master or the person responsible for overseeing the marketing plan owns this layer. This role ensures that all marketing activities are synchronized with the tactical goals.
Reports are reviewed on a monthly basis, allowing for timely adjustments to tactics and strategies as needed.
3. Marketing production metrics (for Production Executives).
These metrics are focused on the execution and outcomes of specific marketing activities and campaigns, tailored for production executives. They measure campaign performance and individual asset effectiveness against activity plans. Reports are reviewed in weekly sprints to facilitate quick adjustments and ensure smooth execution.
This layer is focused on measuring the execution and performance outcomes of individual marketing activities and campaigns. It is operational in nature, ensuring that all tasks are executed as planned.
The benchmarks here are against activity plans, which provide a detailed view of the execution against predefined plans and timelines.
The impact is measured based on the performance of individual assets or activities within a specific campaign, helping to understand what works and what doesn't at a granular level.
The key metrics in this layer include Campaign Metrics, which measure the success of specific campaigns in terms of reach, engagement, conversions, etc.
This layer is owned by the Production Executives Team, who are responsible for the execution of marketing plans and ensuring that campaigns run smoothly.
Reports in this layer are reviewed during weekly sprints, allowing for quick iterations and adjustments to ongoing campaigns.
The importance of role-specific marketing metrics
The FAPI Marketing Framework emphasizes the need for tailored reporting layers at various organizational levels in its marketing metrics layers.
By segmenting reports into Commercial, Management, and Production metrics, the FAPI Marketing Framework ensures that each stakeholder receives relevant insights that are directly aligned with their role and responsibilities.
This approach not only improves the precision of decision-making but also ensures that marketing activities are closely aligned with both strategic and tactical business objectives.
The key takeaway is the importance of matching the right type of marketing report to the right business function, thereby enabling more accurate analysis, better decision-making, and ultimately, more successful marketing outcomes.