Preparing Marketing Data for Decision Making
In modern marketing, data is everywhere. But without structure and purpose, data is just noise. The real value comes when data is prepared in a way that makes it actionable, contextual, and aligned with responsibilities.
As part of the Insights Module in the FAPI Marketing Framework, preparing marketing data for decision making ensures that teams move beyond collection and reporting, and instead focus on clarity, consistency, and meaning.
Why data preparation matters. ensuring reliability and integrity
The primary goal of marketing data preparation (covered in the Data Acquisition component of the Insights Module) is to ensure the marketing team has access to the right data, organized and ready for analysis.
This is a critical leadership responsibility. Within the FAPI Marketing Framework, this responsibility falls to the Plan Master, who must establish benchmarks and key performance indicators (KPIs) and clearly explain their purpose before execution begins.
Getting this right avoids costly misalignment. When teams rely on inaccurate or poorly defined data, they risk making the wrong decisions and allocating resources inefficiently.
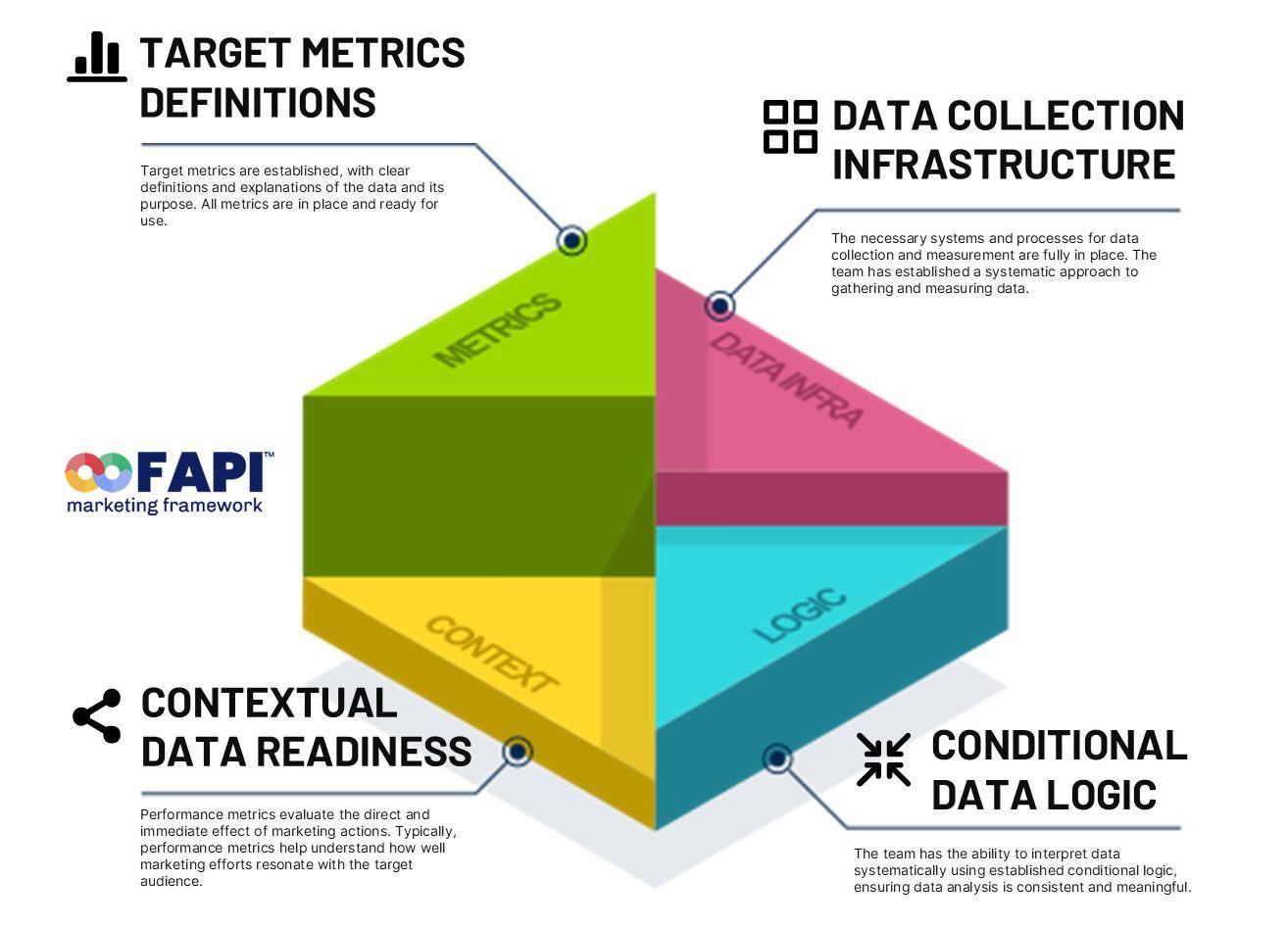
Four Pillars of marketing data readiness
To prepare marketing data properly, four areas must be in place:
1. Target metrics defined and explained
Clear KPIs and benchmarks are established, with definitions that explain both the what (the metric itself) and the why (the purpose it serves). This creates alignment on what the team is working towards and how success will be measured.
2. Data collection infrastructure
Behind every meaningful metric is a solid measurement system. The right processes and tools must be in place to collect, track, and store marketing data consistently. This ensures the team isn’t scrambling to gather information but can rely on an established system.
3. Contextual data readiness
Raw performance data rarely tells the whole story. Contextual inputs, such as historical trends, competitive benchmarks, and industry insights, help decision makers understand results in perspective. Context is what turns data into insight.
4. Conditional data logic
Numbers are only useful if they are interpreted consistently. By applying conditional logic rules for how data is analyzed and compared, teams avoid bias, guesswork, or misinterpretation. This creates meaningful, reliable insights.
Turning data into decisions
When these four elements are in place, marketing data transforms from a reporting exercise into a true decision-making tool. The Plan Master ensures the framework is ready, while the team benefits from clarity and consistency.
Preparing marketing data is not just about being able to measure, it’s about being able to decide. With actionable, contextual, and well-structured insights, marketing leaders can make decisions with confidence, drive better performance, and demonstrate impact.
Visit the FAPI Marketing Academy to explore resources, frameworks, and practical tools that will help you and your team make smarter, data-driven marketing decisions.







