Strategic Structuring of Marketing Departments. Insights from the FAPI Marketing Framework
It is estimated that there are over 130 marketing job roles, based on titles used by organizations of various sizes. Delving into the hierarchy, the distribution includes over 50 roles tailored for staff or individual contributors, more than 60 roles in mid-management or supervisory capacities, and 14 in senior management. This diversity underscores the complexity of marketing functions and the challenges of managing and structuring marketing departments effectively.
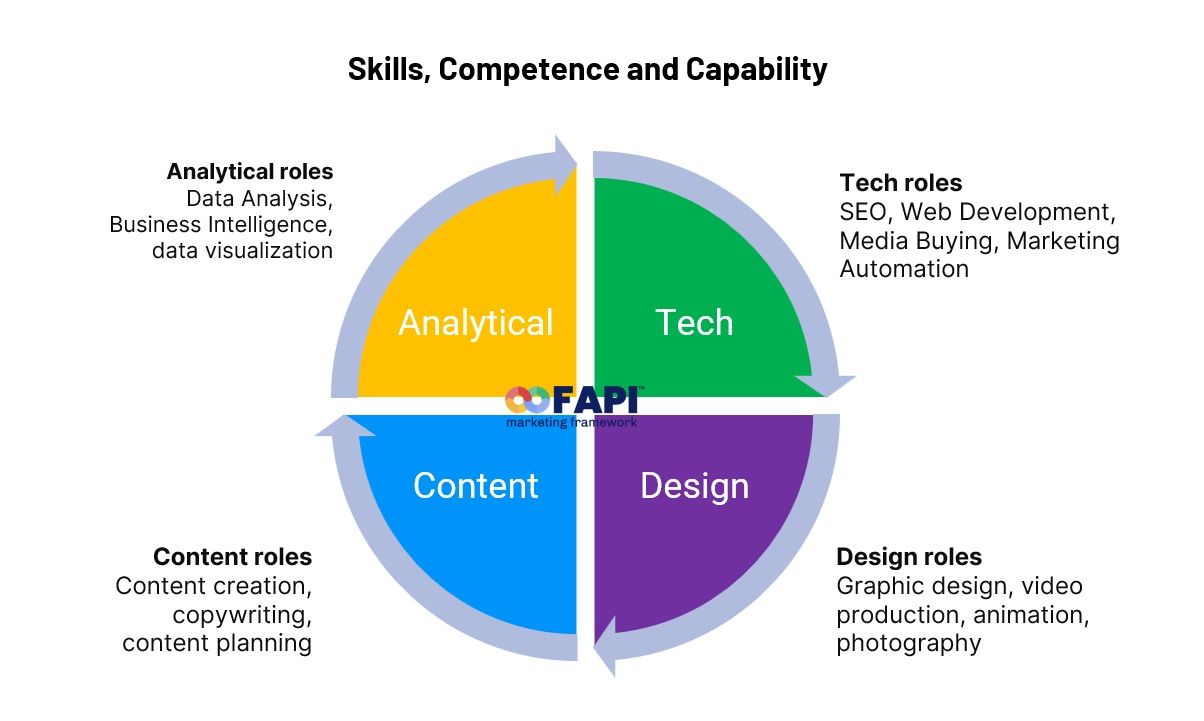
In accordance with the FAPI Marketing Framework within the Architecture module, the Plan Master emphasizes the strategic organization of marketing departments. This approach aligns the department's structure with the best requirements, commercial goals, and strategic plans, ensuring a balanced allocation of resources across
Content, Design, Analytical, and Technical domains. The framework guides the creation of a cohesive and efficient team capable of achieving the organization's marketing objectives.
The following is a comprehensive list of job titles in the marketing industry, categorised by their level of seniority. This list aims to provide a clear understanding of the various marketing roles available, ranging from entry-level positions to executive-level leadership roles.
Staff level marketing roles
These roles typically involve direct execution of tasks with some level of autonomy but are more focused on individual contributions rather than team leadership or strategic oversight.
Account Executive
Affiliate Marketing Manager
Analyst Relations Specialist
Brand Ambassador
Brand Strategist
Campaign Manager
Content Creator
Content Marketing Specialist
Content Specialist
Content Writer
Copywriter
Corporate Communications Assistant
Creative Director
Digital Marketing Consultant
Digital Marketing Specialist
Ecommerce Content Specialist
Ecommerce Marketing Analyst
Email Developer
Email Marketer
Email Marketing Specialist
Engagement Coordinator
Graphic Designer
Insights Analyst
Internet Marketing Specialist
Junior Product Marketing Associate
Market Research Analyst
Market Research Interviewer
Marketing Analyst
Marketing Assistant
Marketing Communications Coordinator
Marketing Communications Specialist
Marketing Consultant
Marketing Coordinator
Marketing Data Analyst
Marketing Specialist
Media Buyer
Media Planner
Media Relations Coordinator
Multimedia Communications Specialist
Partner Marketing Advisor
PPC (Pay Per Click) Manager
Product Research Analyst
Public Relations Intern
Public Relations Specialist
Publicity Assistant
Qualitative Research Assistant
SEM Specialist
SEO Specialist
Social Media Coordinator
Social Media Editor
Social Media Specialist
Video Marketing Specialist
Web Analyst
Web Marketing Specialist
Marketing Research Analyst
Event Marketing Coordinator
Public Relations Manager
Event Planner
Management level marketing roles
These roles typically involve both direct contributions and oversight of teams or projects. They may include strategic planning within specific areas of marketing.
Account Manager
Analyst Relations Manager
B2B Marketing Manager
B2C Marketing Manager
Brand Activation Manager
Brand Manager
Brand Marketing Manager
Channel Marketing Director
Communications Manager
Community Manager
Content Manager
Content Marketing Manager
Content Marketing Producer
Content Director
Content Strategist
Corporate Communications Manager
Corporate Partnership Marketing Manager
CRM Manager
Demand Generation Manager
Digital Brand Manager
Digital Communications Professional
Digital Marketing Manager
Digital Media Manager
Digital Product Marketing Manager
Digital Strategist
Director of Email Marketing
Director of Influencer Marketing and Partnerships
Director of Market Research
Director of SEO Operations
Director of Social Media
E-commerce Marketing Manager
Ecommerce Marketing Manager
Email Marketing Manager
Email Marketing Strategist
Email Operations Manager
Engagement Manager
Event Marketing Manager
Growth Marketing Manager
Influencer Marketing Manager
Loyalty Marketing Manager
Marketing and Promotions Manager
Marketing Communications Manager
Marketing Operations Manager
Marketing Technologist
Online Marketing Manager
Paid Search Manager
Partnership Marketing Manager
Pay-Per-Click Manager
Portfolio Marketing Manager
Product Manager
Product Marketing Manager
SEM Manager
SEO Manager
Social Media Manager
Social Media Marketing Manager
Social Media Strategist
Solutions Marketing Manager
Trade Marketing Manager
Web Content Manager
Web Marketing Manager
Advertising Manager
Senior leadership marketing roles
These roles involve high-level strategic decision-making and leadership, guiding the marketing efforts of entire organizations or large departments.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
Chief Marketing Officer
Director of Brand Marketing
Director of Brand Strategy
Director of Communications
Director of Digital Marketing
Director of Marketing
Director of Product Marketing
Director of Social Media Marketing
Director of Web Marketing
Ecommerce Marketing Director
Head of Marketing
Marketing Director
Partnership Marketing Director
Vice President of Marketing